The Pfizer Foundation Invests in Community-Based Solutions to Combat the Threat of Infectious Diseases

Globally, infectious diseases are responsible for an estimated seven million deaths annually1 and are a leading cause of disability, particularly among young children and marginalized populations,2 often perpetuating the cycle of poverty.3
This is one of the reasons why The Pfizer Foundation* is dedicated to accelerating innovative solutions and improving health systems to help address the urgent threat of infectious diseases. Through the Global Health Innovation Grants (GHIG) program, now in its fifth year, 20 recipients of the one-year program – including non-governmental organizations (NGOs), non-profits, and social enterprises in low- and middle-income countries – will receive $100,000 USD to support community-based initiatives focused on combatting infectious diseases.
Spurred by emerging infections like COVID-19, vulnerable populations in low-resource settings continue to be disproportionately impacted by infectious diseases. Within this evolving landscape, the needs of local communities are dynamic, underscoring the importance of empowering local innovators to identify and address their most important and urgent needs.
“We are dedicated to addressing the most challenging global health needs of our time by supporting innovators around the world, especially in low-resource settings, to help scale innovations, improve health systems, and generate actionable insights,” said Caroline Roan, President, The Pfizer Foundation and Vice President, Global Health and Patient Access, Pfizer, Inc. “As the burden of COVID-19 grows, particularly among marginalized communities, local innovators are bringing new and creative thinking to the fight against infectious diseases. By partnering, we can expedite the development of solutions that help address these healthcare inequities.”
The GHIG program helps to accelerate global health innovations by providing partners with the financial and technological tools to navigate the unique challenges they face in their communities. Since its launch in 2016, the flagship program has provided $9.5 million USD to organizations in 16 countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America. With these funds, The Pfizer Foundation has helped organizations train more than 10,000 staff members and reach more than two million patients through programs aimed at strengthening health systems at the community and primary care level and use of digital technology tools to facilitate improved care.**
Our 2020 grantees are working to make an impact across a range of areas through community-tailored approaches, including responding to the COVID-19 pandemic and future pandemics, reducing child mortality, and addressing antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Examples include:
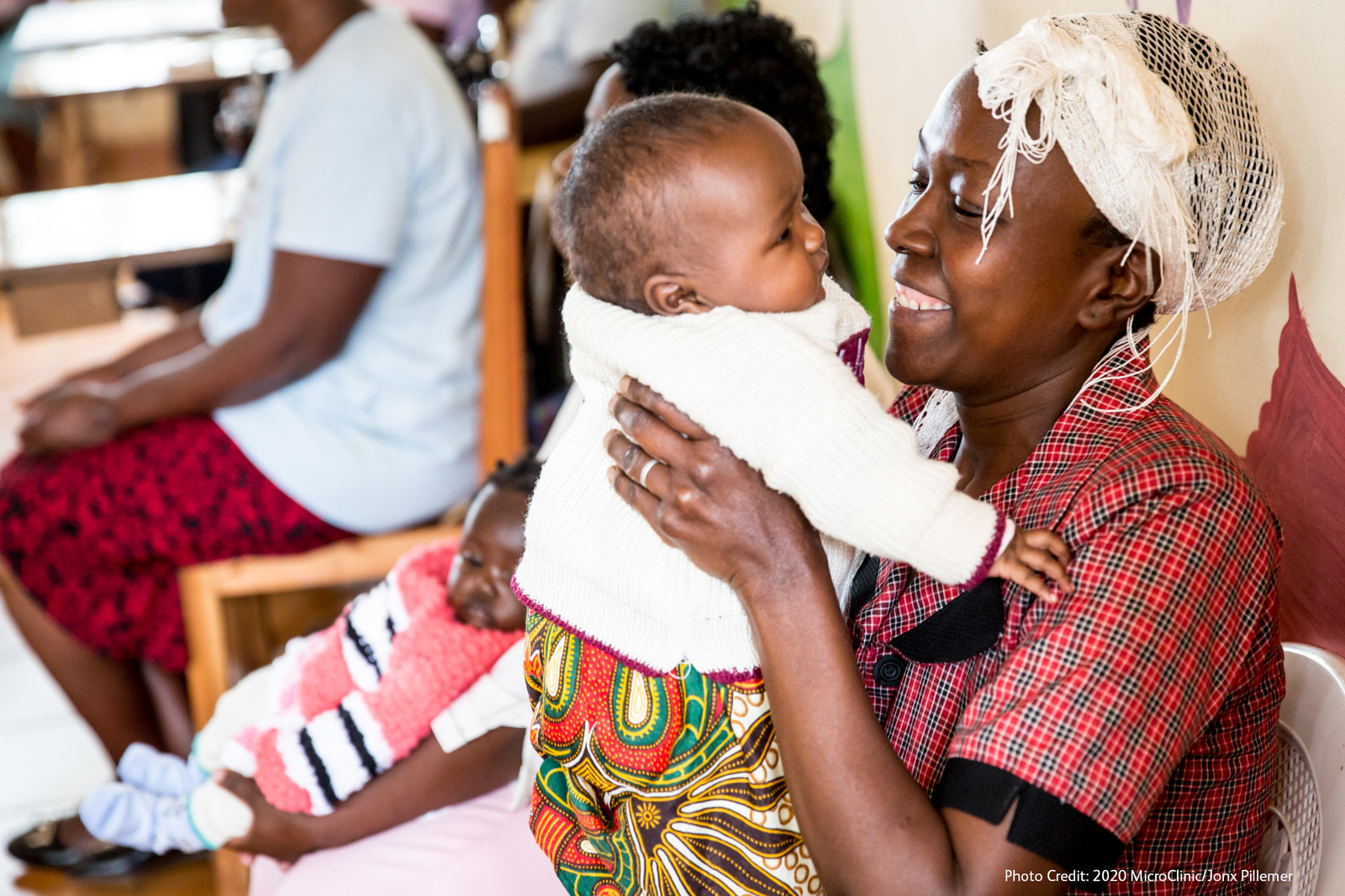
- The enhancement of 2020 MicroClinic Initiative to build capacity for optimizing the testing and treatment of infectious diseases across clinics in Kenya and South Sudan, including influenza, measles, tuberculosis, and COVID-19
- Sevamob’s expansion of mobile clinics in underserved areas throughout India that provide infectious disease screenings and consultation for COVID-19, tuberculosis, Hepatitis C, and HIV
- The deployment of Jacaranda Health’s program in 71 public hospitals across Kenya to provide rapid support to infants and mothers in distress from maternal and neonatal complications, including those caused by infectious diseases
We recognize that innovative local-born solutions have the power to create ripple effects that can transform the healthcare landscape and redefine the way we fight infectious disease. Through these partnerships, we can create meaningful and sustainable solutions that address today and tomorrow’s biggest challenges, bringing equitable and affordable interventions to people who need them most, and help protect the world’s most vulnerable people.
Learn more about the 20 organizations in this year’s cohort:
2020 MicroClinic Initiative (Kenya; South Sudan); Afya Research Africa (ARA) (Kenya); Ayzh (India); Care 2 Communities (Haiti); Fundación ViveCon Bienestar - Bive (Colombia); Group for Technical Assistance (GTA) (Nepal); Health Builders (Rwanda); Jacaranda Health (Kenya); Last Mile Health (Liberia); LifeNet International (Uganda); Living Goods (Kenya; Uganda); Muso (Mali); North Star Alliance (Sub-Saharan Africa); One Family Health (Rwanda); Penda Health (Kenya); reach 52 (Cambodia; Philippines); Sevamob Ventures (India); Society for Nutrition, Education, and Health Action (SNEHA) (India); THINKMD (Nigeria); Unjani Clinics NPC (South Africa).
*The Pfizer Foundation is a charitable organization established by Pfizer Inc. It is a separate legal entity from Pfizer Inc. with distinct legal restrictions.
**GHIG Grantee Outputs Years 1-4 (October 2019 – March 2020)
References:
- Global Burden of Disease Tool [Data set], University of Washington, Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, Global Health Data Exchange, 2020. Accessed September 19, 2020 from http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool.
- World Health Organization. (2008). The global burden of disease : 2004 update. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43942.
- Walker, P., Whittaker, C., Watson, O., Baguelin, M., Winskill, P., Hamlet, A., . . . Ghani, A. (2020, July 24). The impact of COVID-19 and strategies for mitigation and suppression in low- and middle-income countries. Retrieved September 18, 2020, from https://science.sciencemag.org/content/369/6502/413.