Article
Featured Articles
Read our latest stories on the people and scientific innovations making a difference in patients’ lives.
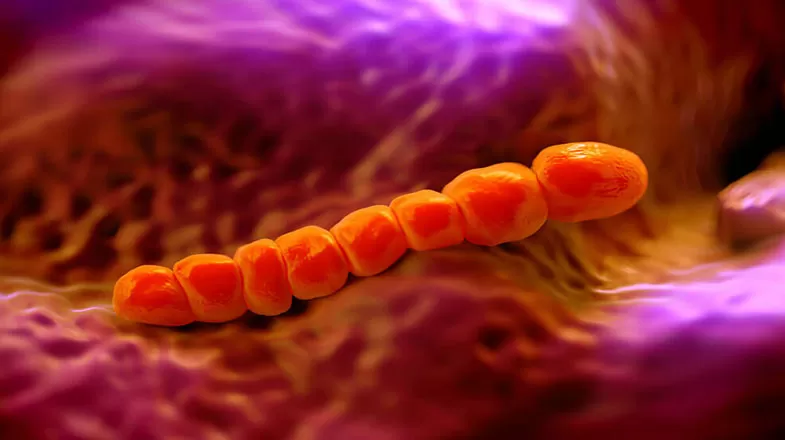
Vaccines to Fight Sugar-Coated Bacteria
Sugar-coating can put a positive spin on things. But when it comes to some bacteria, which cause diseases such as meningitis and pneumonia, their sugar coating is among the traits that make them so dangerous to humans. Read on to learn how scientists have developed a class of vaccines, known as polysaccharide protein conjugate vaccines, that teach the immune system to fight these microbes. But First, Vaccine Basics Vaccines are a powerful public health tool that saves two to three million...
foundations-science
Seeing Science in the Everyday: Glow Sticks That Detect Cancer
Researchers are using the same chemical processes behind glow sticks to make better tools to diagnose cancer. The same science behind glow sticks and the crime scene chemical luminol – which glows blue in the presence of blood – is now being used to develop cutting-edge tools to detect cancer and other medical diagnoses. When you snap a glow stick, two liquids inside the plastic tube come into contact, setting off a chemical reaction that emits energy in the form of light. This process is...
How Genetically Related Are We to Bananas?
Gene sequencing reveals that we have more in common with bananas, chickens, and fruit flies than you may expect. We’ve long known that we’re closely related to chimpanzees and other primates, but did you know that humans also share more than half of our genetic material with chickens, fruit flies, and bananas? Since the human genome was first sequenced in 2003, the field of comparative genomics has revealed that we share common DNA with many other living organisms — yes, including our favorite...
Science Fact or Science Fiction? Lactic Acid Buildup Causes Muscle Fatigue and Soreness
Anyone who has pushed themselves through an intense workout will be familiar with “feeling the burn” — that sensation of fatigue and pain that sets in when you subject your muscles to lifting heavy loads repeatedly or sprinting all-out.This burning sensation is associated with a buildup of acid in the muscles during intense exercise, and lactic acid has long been thought to be the culprit in that acid buildup, known as acidosis. Lactic acid is a byproduct of anaerobic metabolism, in which the...
A New Frontier for AI: Helping Scientists Develop Potential New Medicines
When Google’s artificial intelligence program known as AlphaGo decisively beat the reigning human champion of the ancient board game of Go in a series of high-profile matches in 2016, it was a watershed moment in the field of machine learning. And while much has been made of impressive feats of artificial intelligence (AI), like AlphaGo and self-driving cars, a lesser known fact is that the same techniques are also helping scientists explore potential new medicines. The link between AI and drug...
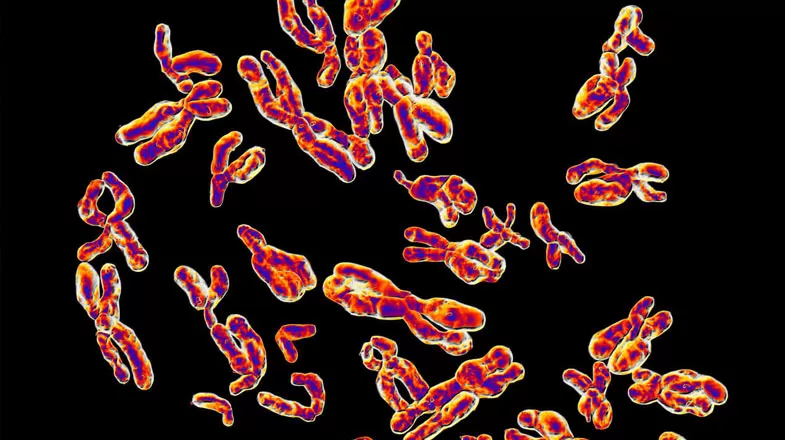
What’s on the Y Chromosome Handed Down From Father to Son?
Among the many things parents hand down to their children are 23 pairs of chromosomes – those thread-like structures in the nucleus of every cell containing the genetic instructions for every person. We inherit a set of 23 chromosomes from our mothers and another set of 23 from our fathers.One of those pairs are the chromosomes that determine the biological sex of a child – girls have an XX pair and boys have an XY pair, with very rare exceptions in certain disorders. Females always pass an X...
This Scientist's Life: Derek Buhl
Meet Derek Buhl, Principal Scientist for Central Nervous System (CNS) medicines at Pfizer’s Kendall Square facility in Cambridge, Mass. Buhl’s subject of research is one of the most complex systems in the known universe – the human brain, and what can go wrong with it, and how to correct problems with the help of novel pharmaceuticals. To explain what he does to a non-scientist, Buhl sometimes quotes what his 6-year-old daughter once said about his work, and how it relates to the work of his...
Bodily Functions Explained: Spicy Food Reaction
Spicy food contains chemicals that trick the body into cranking up its internal air-conditioning system, triggering responses from head to toe and involving everything from the respiratory to the circulatory system.It happens at dinner tables around the world every day. Something spicy — a chunk of chili pepper, perhaps — goes from fork to mouth, setting off a body-wide chain reaction.A burning sensation spreads across the lips and ignites the tongue. Mucous membranes, which protect the lungs...
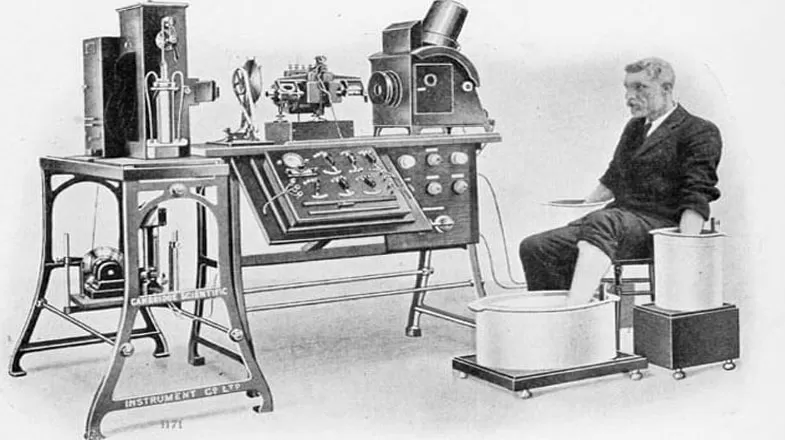
Flashback: The First ECG
p.p1 {margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 12.0px Times} p.p2 {margin: 5.0px 0.0px 5.0px 0.0px; font: 12.0px Times} p.p3 {margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 12.0px Times; min-height: 14.0px} span.s1 {font: 12.0px 'Times New Roman'} Willem Einthoven found the beat and built a machine that could measure the electrical current a heart creates. It weighed 600 pounds. An electrocardiogram — called informally an ECG or EKG — measures the small electric waves that a human heart creates. It’s...
The Great Migration: Tracking Immune Cells’ Travels
Scientists are studying how immune cells move to develop better treatments for autoimmune diseases. Birds migrate. People migrate. And so do cells. T-cells squeezing between collagen fibers. PLOS ONE/Coles JA Our immune cells, in particular, are always on the move, constantly patrolling the body for foreign invaders. If an unwelcome visitor enters through the nose, mouth or eyes, or there’s a break in the skin, these nimble soldiers are ready to flood the attack site and send out signals...
advancing-medical-research
Fixing Broken Body Clocks
By finding ways to restore sleep rhythms, researchers can benefit Alzheimer’s patients and others. Every living being from fungi to frogs has an internal clock that normally runs on a 24-hour cycle. In humans, this master clock resides in a tiny region of the brain’s hypothalamus and controls everything from hunger and sleep patterns to daily hormone fluctuations and body temperature. The brain’s master clock sets the tempo for the rhythms of every cell throughout the whole body. “It’s like...
advancing-medical-research
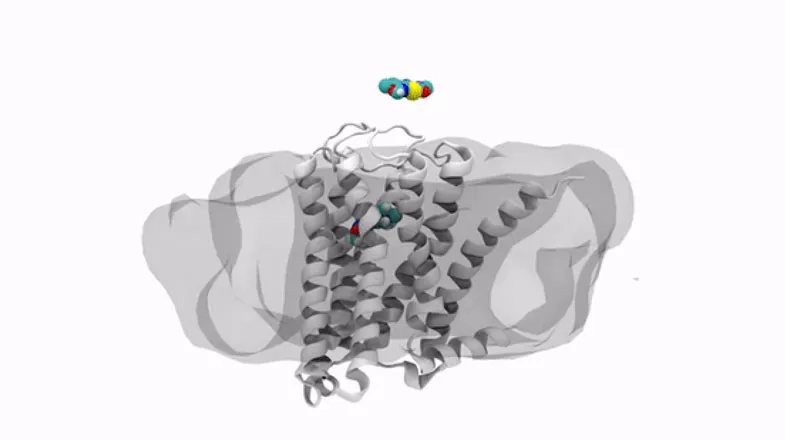
3-D Molecules Move into the Fast Lane
Seeing compounds in three dimensions clears a path for making medicines faster, better. Understanding how medicines behave around human cells was once a matter of educated guesswork, in large part because how they act at the molecular level isn’t visible. But today, structural biology and computational chemistry – or the use of computer modeling and molecular dynamics simulation – take medicine design into the next dimension. Well, to be precise, the third dimension. With the jump into 3-D...
Media Resources & Contact Information
Anyone may view our press releases, press statements, and press kits. However, to ensure that customers, investors, and others receive the appropriate attention, Pfizer Media Contacts may only respond to calls and emails from professional journalists.