Article
Featured Articles
Read our latest stories on the people and scientific innovations making a difference in patients’ lives.
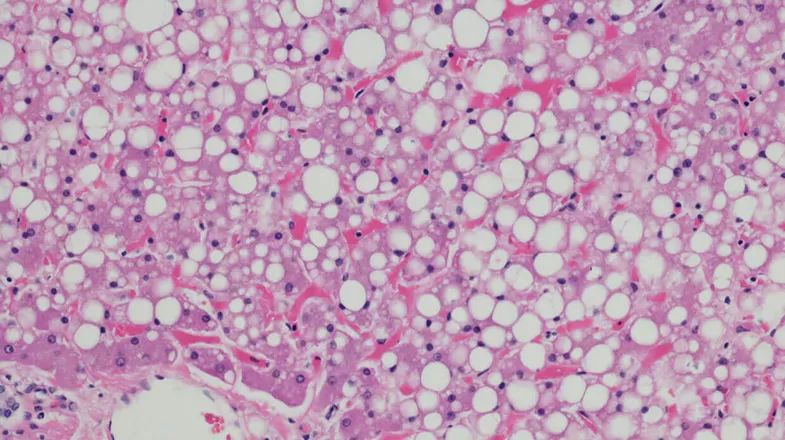
International Project to Help Detect a Liver Disease Called NASH Gets $35M Boost
Imagine if the only way to know whether you have diabetes was for a doctor to take a biopsy of your pancreas, rather than being able to check your glucose levels using a simple blood test. That is the current state of affairs for a disease known as NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis) in which the liver is damaged by inflammation due to a buildup of fats. NASH is a progressive subtype of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Associated risk factors for NAFLD, NASH and the later stages of...
Test Tube Ancestors: The Science of Genetic Testing in Genealogy
Genetic testing companies use complex methods to determine your ancestry. But how accurate are they? For any two people in the world, 99.5 percent of their DNA is identical (99.9 percent for any two people of the same sex), yet it’s only human to latch on to that 0.5 percent and seek out what makes you special. As of 2016, nearly 3 million genetic ancestry tests have been sold, thanks in part to popular TV shows in which celebrities delve into their genealogy using both their genome and...
Treating Cancer by Using Epigenetics, the ‘Software’ of Our Genes
All of our cells possess the same set of DNA. So, why is it that some cells turn into skin cells while other cells turn into lung cells — and still other cells go rogue and turn into cancer cells? The key lies in the epigenome — the naturally occurring chemical markers that accompany your genes and act as molecular switches that can turn a gene on or off without changing your DNA itself. For example, in agouti mice, even identical twin siblings with the same DNA can have different fur colors...
The Science Behind the Winter Blues
As the days grow darker and colder, many of us occasionally experience the winter doldrums. A small percentage of the US population (about 1 to 10 percent, depending on where you live), however, suffers a more severe form of the blues known as seasonal affective disorder (SAD), with symptoms such as feeling sluggish, agitated, hopeless, overly fatigued and changes in appetite. In the U.S., the prevalence of SAD is linked to how far north you live. The incidence of SAD is nearly 10 percent of the...
Are Genetic Tweaks Made by Gene Therapy Handed Down to Offspring?
The possibility of finding a treatment or even a cure for genetic disorders such as muscular dystrophy or hemophilia has taken a giant leap forward in recent years with the advent of gene therapy as a way to modify a defective gene or group of genes. But would those changes be handed down to that person’s offspring? In general the answer is no, except in a very specific circumstance that isn’t being pursued by pharmaceutical researchers as a potential therapy. But to understand why those...
The Search for a ‘Liquid Biopsy’ and Other Advances to Diagnose Cancer
A liquid biopsy — a technology that attempts to diagnose a disease through a blood sample rather than by using a tissue sample collected through a traditional biopsy — is just one technology being explored to make cancer diagnosis faster and less invasive. Imagine going to your doctor for a simple blood test and knowing within 24 hours whether you have cancer. No need for biopsies, time-consuming scans, and waiting days, if not weeks, to learn results. For scientists like Dr. Hakan Sakul...
Metabolism and Immunology: Using Lessons From Metabolic Diseases to Treat Autoimmune Disorders
By regulating the metabolism of immune cells, researchers are uncovering novel ways to suppress inflammation and treat autoimmune diseases. Scientists have long recognized that metabolic-related disorders such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes and obesity have links to inflammation. But what if the converse were also true? What if inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease had a metabolic component to them? In recent years, researchers in the burgeoning...
Feasting on Science: Decoding Thanksgiving Dinner
Thanksgiving is an occasion to appreciate family, friends and, most importantly, food. Many of us celebrate by indulging a little too much and perhaps dozing off on the couch. This year, how about getting into the Thanksgiving spirit by taking a closer look at some of our favorite holiday staples and seeing what science tells us about them. From the yeast in the bread to the tryptophan in the turkey, there’s more to a Thanksgiving feast than initially meets the eye. Tryptophan in the Turkey I...
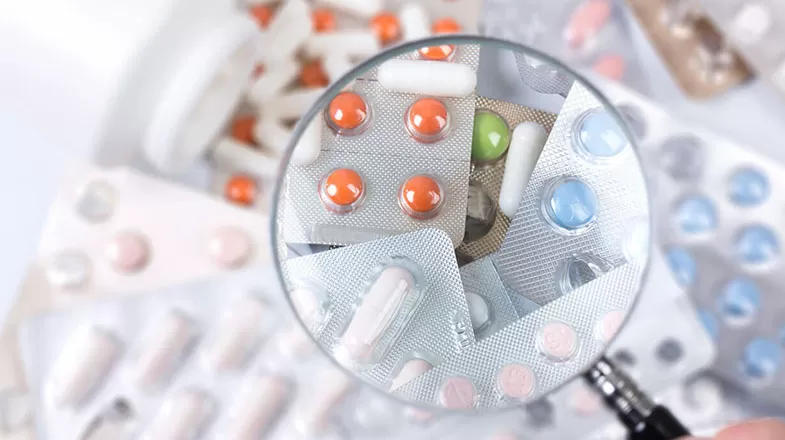
4 High-Tech Tools That Help Investigators Detect Counterfeit Medicines
The issue of counterfeit medicines has been an enduring problem, especially in lower income countries, where an estimated 10 to 30 percent of medicines sold are believed to be counterfeit, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In higher income nations with stricter regulations, including the United States and countries in the European Union, an estimated 1 percent of medicines sold are counterfeit, according to the CDC. In addition to the economic impact...
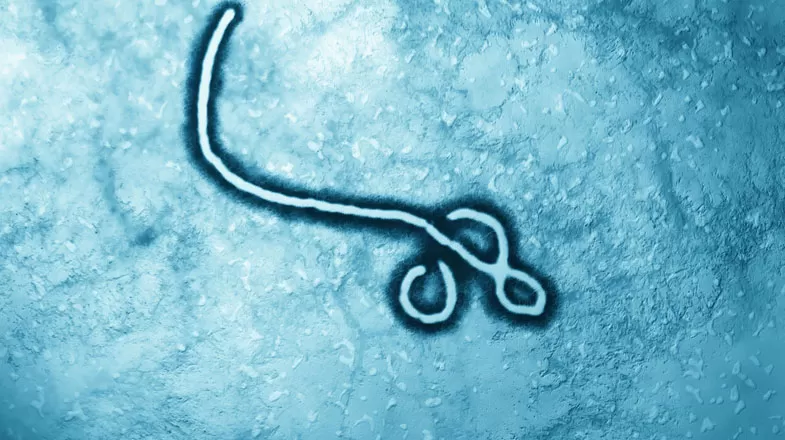
What Is a Virus and What Makes Them Both Fearsome and Useful?
Even people who are in the best of health occasionally battle the common cold or the flu — both caused by viruses. In the case of the common cold, the rhinovirus is most often the culprit. In the case of the flu, it’s the various permutations of the influenza virus. And those are just two types in a panoply of viruses that inhabit our world, including polio, rabies, Zika and Ebola. But what exactly is a virus? How is it different from bacteria? And how can a microbe that is believed to be one...
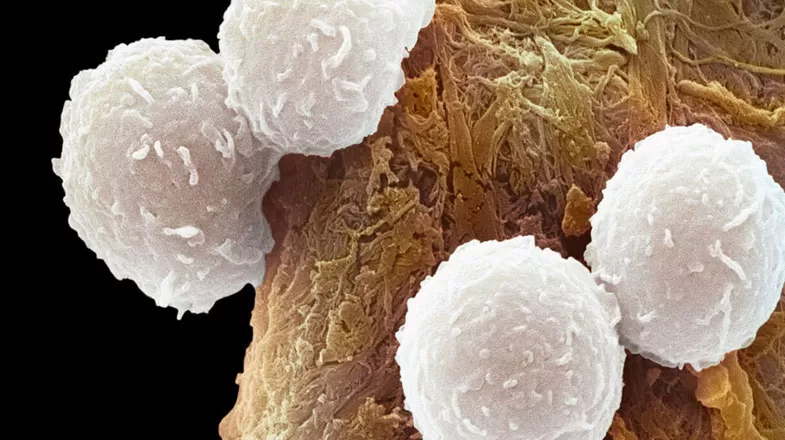
How Immuno-Oncology Taps Into the Body’s Own Immune System to Fight Cancer
Traditional approaches to fighting cancer such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy have saved countless lives over the years, but they are often accompanied by debilitating side effects because they also kill healthy cells in addition to attacking the malignant cells. One of the most important advances in cancer therapies is a field known as immuno-oncology, which uses methods that tap into a patient’s own immune system to detect and destroy cancer cells. Experts predict that immuno-oncology...
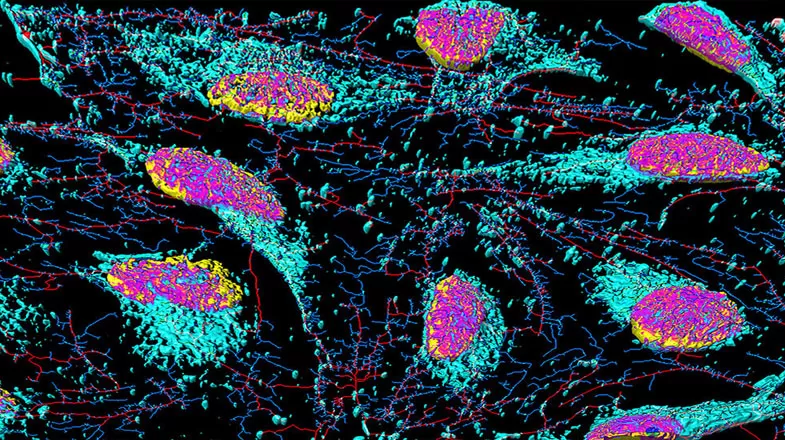
Advanced Culture: Making More ‘Life-Like’ Cellular Models
Cellular models, an essential part of developing new medicines, are becoming more realistic and relevant to patients. Long before a drug candidate enters clinical trials to be tested in humans, it goes through countless rounds of testing over several years in cellular models, also known as cell-based assays. From the earliest stage of identifying active molecules that can interact with a disease target to the later stages of testing toxicity and dosing, cells, particularly human cells, are...
Media Resources & Contact Information
Anyone may view our press releases, press statements, and press kits. However, to ensure that customers, investors, and others receive the appropriate attention, Pfizer Media Contacts may only respond to calls and emails from professional journalists.